What is pricing?
Pricing is the process of determining what a company will receive in exchange for a product or service. 💲
It involves setting a monetary value that customers are willing to pay, and it encompasses several strategies and factors, including production costs, market demand, competition, and the company's overall objectives.

Pricing: a quick glossary
Let's break down some common pricing terminology to understand the nuances... 🔎
Cost and price
The first and most important difference is between "price" and "cost".
- Price is the amount charged by a company for its product or service.
- Cost is the money required to produce that product or service.
Ideally, the price is higher than the cost, but that's not always the case. For example, a company may lower its price below its profit margin to stay competitive or attract more customers.
⏳ In the long term, regardless of the strategy, a company's production costs must be lower than the sales price for the business to be sustainable.
Gross and net margin
Margin is the percentage added to the production cost to determine the final price. For example, if production costs $10 and the margin is 50%, the sale price will be $15. 👛
There are 2 common types of margin:
-
Gross (commercial) margin is the difference between the product's sale price and its cost, divided by the sale price. It shows how much a company earns on each sale before deducting operating expenses.
-
Net (profit) margin is the profit after all operating expenses, interest, and taxes have been deducted from total revenue. Expressed as a percentage of net sales, it reflects how much a company truly earns on each euro of sales. 💶
Catalogue price
The catalogue price is the retail price recommended by the manufacturer, but it's not necessarily the final price chosen by the retailer.
It is generally based on factors such as production costs, competition, and market demand.
Retail price
The retail price is the price customers actually pay for a product. It is determined by the retailer, who sells the product to the end user.
Wholesale price
The wholesale price is the discounted price at which a product is sold to retailers or distributors. These intermediaries then apply a markup when reselling the product to customers.

Price structure
While pricing refers to the overall approach to setting prices, the price structure is the specific way a company organizes and bills for what it sells.
For complex products such as software and services, the price structure is crucial. It may include the following elements:
-
Tiers and packages - Different levels of value at different price points.
-
Usage-based pricing - Billing based on consumption or usage (e.g., metered rates).
-
Users/subscribers - A price per person using the product over a set period, either as a base price or tied to a package.
-
Contracts - Short-term (e.g., monthly) or long-term (e.g., annual) contracts. Longer contracts usually come with discounted pricing.
-
Ad hoc costs - One-time or recurring fees that go beyond the base price (e.g., software etup or installation).
The importance of pricing in business strategy
Let's explore the specific business areas impacted by pricing... 🕵️
Revenue and business viability
The most obvious impact of pricing is on a company's bottom line. If you can't sell your product for more than it costs to produce, you'll never be able to sustain your business over the long term.
Pricing optimization is about finding the balance between charging the highest possible price and identifying the optimal price that maximises demand. ⚖️
Brand perception and customer value
Pricing also shapes how customers perceive your brand. The two go hand in hand.
- If you're selling to a high-end market, a low price may signal that your product is of mediocre quality.
- At the same time, price-sensitive customers often care less about quality - they're primarily looking for affordability.
In many cases, ustomers don't know what a product is truly worth. Techniques like price anchoring and psychological pricing (e.g., $9.99 instead of $10) help influence buying decisions.
Definition
Anchoring is a
cognitive bias that leads consumers to rely on the
first piece of information they see when evaluating a price. For example, showing a crossed-out original price before the discounted price creates the impression of a better deal - since buyers subconsciously compare the current price to the initial price. 🏷️
Market position and competitive advantage
Beyond digital value, there are many ways to justify the set price of your product or service.
Since customers often don't know the exact monetary value of solving a problem or fulfilling a need, you have to remind them why they're buying in the first place.
-
Brand image has an impact on how customers feel when they buy and use your product.
- Salespeople play a key role in helping customers understand what they're getting for their money - often by highlighting return on investment).
Sales volume and demand
Price sensitivity plays a major role on consumer decision-making.
Your capacity to set prices that reflect your product's value - and match your customers' willingness to pay - is essential to maximizing demand.
Key factors to consider when setting prices
Before setting the final price of your product, several factors must be taken into account:
Production costs
The first and most obvious factor to consider is production cost. Your margins must be sufficient to cover all your fixed and variable costs while still generating a profit.
.jpg)
Target market and customer behaviour
It's essential to know who your target customers to set the right price. The amount they are willing to pay varies significantly depending on factors such as income level, geographic location, and lifestyle.
You also need to consider their purchasing behaviour. What motivates them to buy? Are they willing to pay more for convenience? Do they care about brand image or product quality?
Competitors' pricing strategies
Although competitors shouldn't dictate your decision, they still serve as a useful reference point.
Here are a few reasons why:
- If customers are already accustomed to a certain pricing structure, you may be more difficult to get them to accept a different one.
- If your competitors sell a similar product, pricing yours too high or too low can impact perceived value - and therefore willingness to pay.
Business objectives
Depending on your business model, growth stage, and future goals, your pricing strategy will vary.
Product value proposition and differentiation
What problem does your product solve for customers? How well does it meet their needs? Your value proposition is a key factor in determining the value customers assign to your product - and how much they are willing to pay for it.
Additionally, there are several ways to differentiate your product. Product development, marketing, and customer service can all influence how buyers perceive your offer.
How to conduct a price analysis?
Pricing analysis involves evaluating all the factors mentioned above to determine the best price for your product or service.
Here is a basic framework you can use... 👇
1. Identify your direct and indirect competitors
Direct competitors are companies offering a similar product or service to the same customer base.
Indirect competitors offer different products but target the same market or solve the same problem.
2. Research competitors' characteristics and pricing models
Study the pricing models used by your competitors. How do they structure their pricing (e.g., tiered plans, additional fees, usage-based pricing)?
Pay attention to how often they run promotions, how they communicate pricing, and the techniques they use to drive conversions.
3. Analyze your target customers and their purchasing behaviour
The next step is to collect data on your target audience. To do this, you can:
- Conduct surveys and questionnaires. 📝
- Use focus groups.
- Track customer journeys.
- Analyze the purchase history of existing customers.
- Request feedback and customer opinions. 💬
- Monitor mentions and reviews on social media.
- Analyze your website metrics. 📊
- Run A/B tests by offering your product to two different groups at different prices and comparing the results.
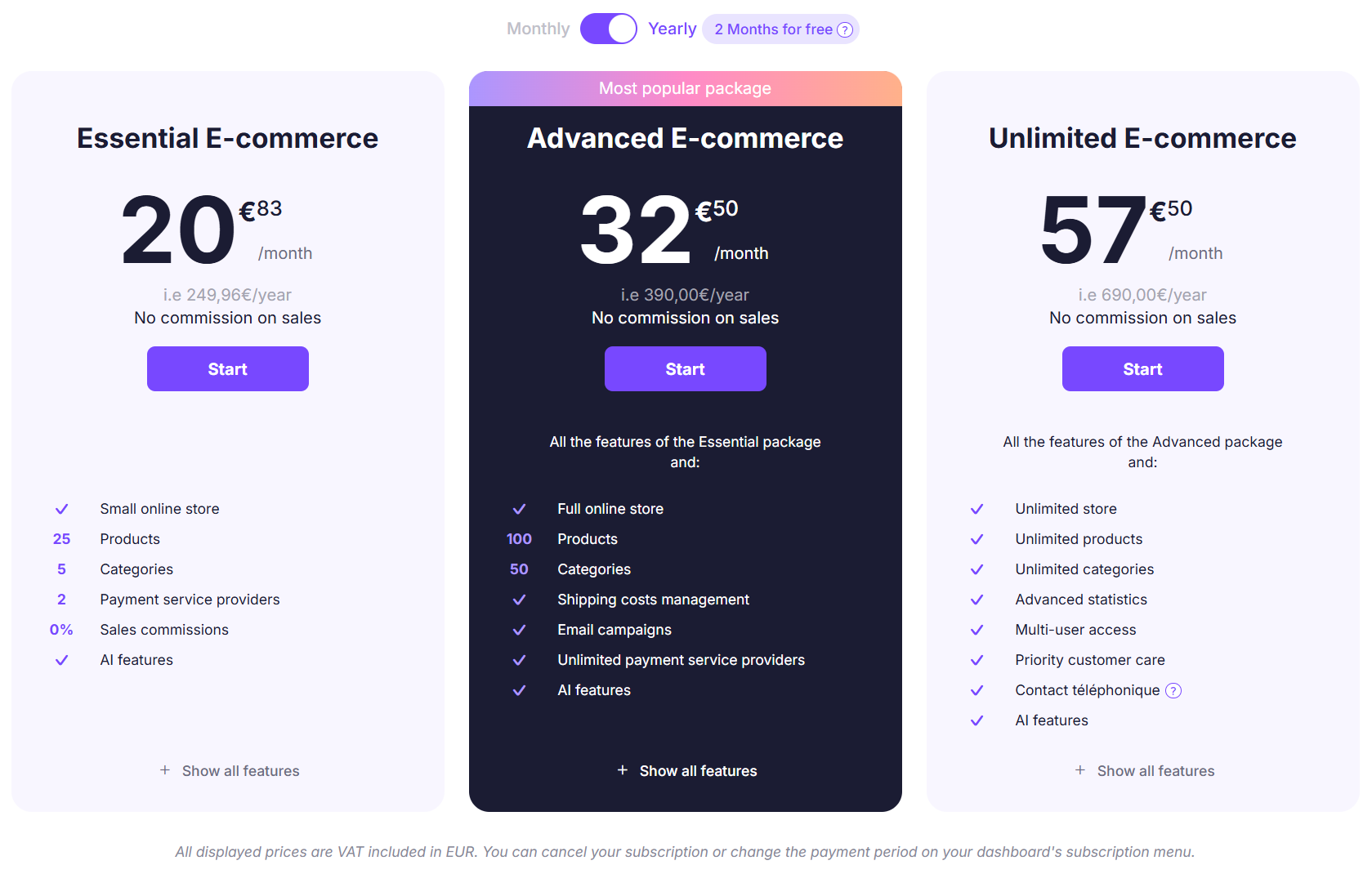
Create your online store
4. Calculate your production and operating costs
To set a profitable and competitive price for your product, it's essential to understand your production and operating costs. 🎯
Start by listing all your direct costs, such as:
- Raw materials
- Labor
- Production supplies
Then, account for all your indirect costs, which include rent, salaries of non-production staff, marketing expenses, and other operating fees.
Add up all these costs, categorize them into fixed and variable expenses, and calculate your break-even point: Break-even point = Total fixed costs / (Price per unit - Variable cost per unit)
5. Evaluate your product's price elasticity
To determine the fair price of a product, companies must also understand how pricing changes affect demand. This is known as price elasticity of demand.

The best way to measure it is by conducting price variation tests and analyzing sales data before and after the changes.
For each price change, calculate the percentage change in quantity sold and the percentage change in price.
Then apply the following formula:
Price elacticity of demand = (% change in quantity sold) / (% change in price)
👉 If elasticity is high (result greater than 1), small changes in price will lead to significant changes in customer demand.
👉 If elasticity is low (result less than 1), price increases may lead to higher profits, as demand remains relatively stable.
👆 Keep in mind that elasticity can vary across market segments and time periods. Use segmentation to analyse elasticity among different customer groups for deeper insights.
7 common pricing strategies
Let's take a look at 7 of the most common pricing strategies...
1. Value-based pricing
This strategy consists of setting prices based on what consumers believe your product is worth.
To succeed with value-based pricing, you need to build a brand centered on benefits, features, and unique selling points. It typically requires significant investment in marketing, research, and public relations.
Example
Value-based pricing is often used for
luxury products like high-end shoes. These brands use marketing to convey a sense of status. When the strategy works, consumers are willing to pay a premium to access the product. 👠💍
2. Competitive pricing
In this approach, you set your prices based on those of your competitors.
Here are some common competitive pricing techniques:
-
Parity pricing: Setting the same price as competitors.
-
Premium pricing: Setting a higher price to signal higher quality.
-
Discount pricing: Offering lower prices or promotional discounts to match or outperform competitors.
.jpg)
3. Price skimming
This strategy involves launching a product at a high price when it enters the market. It communicates premium quality and creates an exclusive experience for early adopters willing to pay more. Over time, the price is gradually reduced to make the product accessible to a broader audience.
Example
Tech companies often use price skimming when launching innovative products. The initial price is high, targeting customers eager to gain early access. As demand spreads,
the price is progressively lowered to reach more users. 📉
4. Cost-plus pricing
Also known as markup pricing, this method involves adding a profit margin to the production cost to determine the final price.
It's commonly used in retail, where a company calculates the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and then adds a markup percentage to ensure a profit.
There are two main types of cost-plus pricing:
-
Full (or traditional) cost pricing includes both direct costs into consideration (e.g. materials and labor) and indirect costs (e.g. marketing rent, administration).
-
Variable cost pricing considers variable costs, excluding fixed overhead like rent. It's better suited to companies with fluctuating production volumes, material costs, or temporary labor.
5. Penetration pricing
In competitive markets, it can be challenging for new companies to establish themselves.
One common way to promote a new product is to offer lower prices than competitors - this is known as penetration pricing.
Example
Many internet service providers use this strategy. They
enter the market with low prices to attract attention. Once they've captured market share and built brand recognition, they gradually shift to competitive pricing.
6. Economicy pricing
This strategy is widely used in markets for basic or generic products.
The goal is to offer lower prices than competitors and generate profit through high sales volume rather than large margins.
7. Dynamic pricing
In some sectors, companies adjust their prices constantly to match current demand - this is known as dynamic pricing.
This approach isn't suitable for all industries, but it works well for sectors like transportation or hospitality, which experience high and low seasons. 📅

Pricing is more than a simple calculation - it's an alchemy between perception, psychology, and strategy.
By using the right levers, you can turn a number into a powerful trigger for purchase. 🚀




.jpg)



.jpg)
